Page 681 - Mastik®
P. 681
Friction and friction coefficients
The friction coefficients μGes, μG, μK dis- finish (depth of roughness), the surface out oil, molybdenum disulfide, molycoat
play variations since they are depen- treatment (naked, blackened, galvani- paste, anti-friction coating etc)! The fol-
dent on several factors, e.g. the material cally zinc coated, dachromatized, etc.) lowing tables give friction coefficients for
combinations, the quality of the surface and the method of lubrication (with/with- threads and for bearing surfaces.
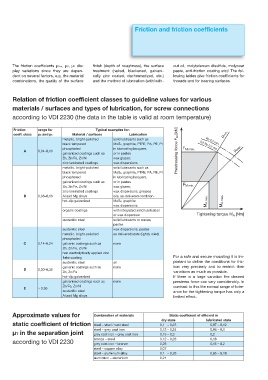
Relation of friction coefficient classes to guideline values for various
materials / surfaces and types of lubrication, for screw connections
according to VDI 2230 (the data in the table is valid at room temperature)
Friction range for Typical examples for:
coeff. class μG and μK Material / surfaces Lubrication μ min.
metallic, bright-polished solid lubricants such as Rp 0,2 min.
black tempered MoS2, graphite, PTFE, PA, PE, Pl 0,9 Rp 0,2 min.
phosphated in lubricating lacquers, F M max. μ max.
A 0,04–0,10 Prestressing force F M [kN]
galvanized coatings such as or in pastes
Zn, Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni wax glazes;
zinc laminated coatings wax dispersions
metallic, bright-polished solid lubricants such as
black tempered MoS2, graphite, PTFE, PA, PE, Pl
phosphated in lubricating lacquers,
galvanized coatings such as or in pastes
F M min.
Zn, Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni wax glazes;
zinc laminated coatings wax dispersions, greases
B 0,08–0,16 Al and Mg alloys oils, as-delivered condition
hot-dip galvanized MoS2; graphite M A min. M A max.
wax dispersions
organic coatings with integrated solid lubrication
or wax dispersion Tightening torque M A [Nm]
austenitic steel solid lubricants or waxes;
pastes
austenitic steel wax dispersions, pastes
metallic, bright-polished as delivered state (lightly oiled)
phosphated
C 0,14–0,24 galvanic coatings such as none
Zn, Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni
non electrolytically applied zinc
flake coating For a safe and secure mounting it is im-
austenitic steel oil portant to define the conditions for fric-
galvanic coatings such as none tion very precisely and to restrict their
D 0,20–0,35
Zn, Zn/Fe variations as much as possible.
hot-dip galvanized If there is a large variation the desired
galvanised coatings such as none prestress force can vary considerably. In
Zn/Fe, Zn/Ni contrast to this the normal range of toler-
E ≥ 0,30
austenitic steel ance for the tightening torque has only a
Al and Mg alloys limited effect.
Approximate values for Combination of materials Static coefficient of efficient in
dry state lubricated state
static coefficient of friction steel – steel / cast steel 0,1 – 0,23 0,07 – 0,12
steel – grey cast iron 0,12 – 0,24 0,06 – 0,1
μT in the separation joint grey cast iron – grey cast iron 0,15 – 0,3 0,2
bronze – steel 0,12 – 0,28 0,18
according to VDI 2230 grey cast iron – bronze 0,28 0,15 – 0,2
steel – copper alloy 0,07
steel – aluminium alloy 0,1 – 0,28 0,05 – 0,18
aluminium – aluminium 0,21