Page 682 - Mastik®
P. 682
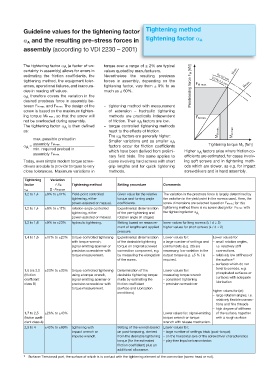
Guideline values for the tightening factor Tightening method
and the resulting pre-stress forces in tightening factor A
A
assembly (according to VDI 2230 – 2001)
The tightening factor A (a factor of un- torque over a range of ± 2% are typical
certainty in assembly) allows for errors in values quoted by manufacturers. μ min.
estimating the friction coefficients, the Nevertheless the resulting prestress Rp 0,2 min.
tightening method, the equipment toler- forces in assembly, depending on the 0,9 Rp 0,2 min.
ances, operational failures, and inaccura- tightening factor, vary from ± 9% to as Prestressing force F M [kN] F M max. μ max.
cies in reading off values. much as ± 60%.
therefore covers the variation in the
A
desired prestress force in assembly be-
tween FM max. and FM min. The design of the – tightening method with measurement
screw is based on the maximum tighten- of extension – hydraulic tightening
ing torque MA max., so that the screw will methods are practically independent
F M min.
not be overloaded during assembly. of friction. Their A factors are low.
The tightening factor is then defined – torque controlled tightening methods
A
as: react to the effects of friction. M A min. M A max.
The A factors are generally higher:
max. possible preload in Smaller variations and so smaller A
assembly FM max. Tightening torque M A [Nm]
= factors occur for friction coefficients
A
min. required preload in
which have been derived from prelimi- Higher factors arise where friction co-
A
assembly FM min.
nary field trials. The same applies to efficients are estimated, for cases involv-
Today, even simple modern torque screw- cases involving hard screws with short ing soft screws and in tightening meth-
drivers are able to provide torques to very grip lengths and for quick tightening ods which are slower, as e.g. for impact
close tolerances. Maximum variations in methods. screwdrivers and in hand assembly.
Tightening Variation
factor FM Tightening method Setting procedure Comments
A 2 · FM middel
1,2 to 1,4 ±9% to ±17% Yield-point controlled Given value for the relative The variation in the prestress force is largely determined by
tightening, either torque and turning angle the variation in the yield point in the screws used. Here, the
power-assisted or manual. coefficients. screw dimensions are selected based on FM min.; for this
1,2 to 1,4 ±9% to ±17% rotation-angle controlled Experimental determination tightening method there is no screw design for FM max. with
tightening, either of the pre-tightening and the tightening factor A.
power-assisted or manual. rotation angle (in stages)
1,2 to 1,6 ±9% to ±23% hydraulic tightening. Setting based on measure- lower values for long screws (lk / d ≥ 5)
ment of lengths and applied higher values for short screws (lk / d ≤ 2)
pressure.
1,4 to 1,6 ±17% to ±23% torque-controlled tightening Experimental determination Lower values for: Lower values for:
with torque wrench, of the desirable tightening a large number of settings and – small rotation angles,
signal-emitting spanner or torque on original screwed control tests (e.g. 20) are i.e. relatively stiff
precision screwdriver with connection component, e.g. necessary; low variation in the connections.
torque measurement. by measuring the elongation output torque (e.g. ±5 % ) is – relatively low stiffness of
of the screw. required. the surface 1)
– surfaces which do not
tend to corrode, e.g.
1,6 bis 2,0 ±23% to ±33% torque-controlled tightening Determination of the Lower values for:
phosphated surfaces or
(friction using a torque wrench, desirable tightening torque measuring torque wrench
surfaces with adequate
coefficient signal-emitting spanner or made by estimating the – consistent tightening
lubrication
class B) precision screwdriver with friction coefficient – precision screwdriver
torque measurement. (surface and lubrication
higher values for (at):
conditions).
– large rotation angles, i.e.
relatively flexible connec-
tions and fine threads
– high degree of stiffness
1,7 to 2,5 ±26% to ±43% Lower values for: signal-emitting of the surface, together
(friction coeffi- torque wrench or torque with a rough surface
cient class A) wrench with release mechanism.
2,5 to 4 ±43% to ±60% tightening with Setting of the wrench based Lower values for:
impact wrench or on post-torqueing, derived – large number of settings trials (post-torque)
impulse wrench. from the desirable tightening – on the horizontal axis of the screwdriver characteristics
torque (for the estimated – play-free impulse transmission
friction coefficient) plus an
additional allowance.
1) Surface: Tensioned part, the surface of which is in contact with the tightening element of the connection (screw head or nut).